Analyze data in RDS and DynamoDB with Amazon Athena Federated Query
Recently I was working on a project which leveraged both Amazon RDS and DynamoDB for different data accessing and persistence scenarios. Overtime, as more users onboarded, there is an increasing demand on analyzing data to generate business insight.
Understand requirements by Personas
In any project that requires certain level of data analytics, it is always critical to understand that people from different perspectives will look at data in different aspects, using different tools, in different frequencies.
For example:
- Management team may prefer to review a group of KPI like revenue, profit (aspect) on a web-based (tool) dashboard weekly or monthly (frequency) .
- A data analyst may feel more comfortable to digging out why sales is declining in a certain area (aspect) with an interactive analytics tool like Tableau or Power BI (tool)
- A customer may just need to track the real-time (frequency) logistics status for a specific order (aspect) on a mobile app (tool). Unlike previous two OLAP examples, this is more like an OLTP scenario.
A typical persona in Data Analytics project

Our challenge
As a new project, the analytics requests were quite ad-hoc. People came with some questions at first place and then more questions afterwards. These questions vary from how many users have registered so far to how long it takes to complete a certain workflow.
Without a proper self-service tool, these requests typically ended up with manual database queries performed by our support engineers on behalf of users. And the results were sent back to users in raw data form of csv files.
This approach is straight forward and practical in short term. However, it comes with a few issues:
- Analyzing data in DynamoDB tables is more complicated than relational database. Usually we need dump a table to csv and manually slice and dice the result
- Joining query with DynamoDB data and RDS data is even more complicated. This typically requires dumping multiple tables into csv and manipulate them in Excel
- The process is manual and not repeatable
Solution
After investigating a number of possible solutions, there seems to be 2 major options:
- Using an ETL job (e.g. AWS Glue job) or a CDC (Change Data Capture) solution to move data from multiple sources to single place, which could be a data warehouse (e.g. Redshift) or a data lake. Then we can use any BI (Business Intelligence) tool like Tableau, Power BI to analyse data.
- Using a lightweight solution to query data in place
The first option usually requires a large amount of effort and investment. Given that we don’t have a clear vision on how far this analytics work will go, it makes sense to pick up the second, quick-win option.
Amazon Athena Federated Query
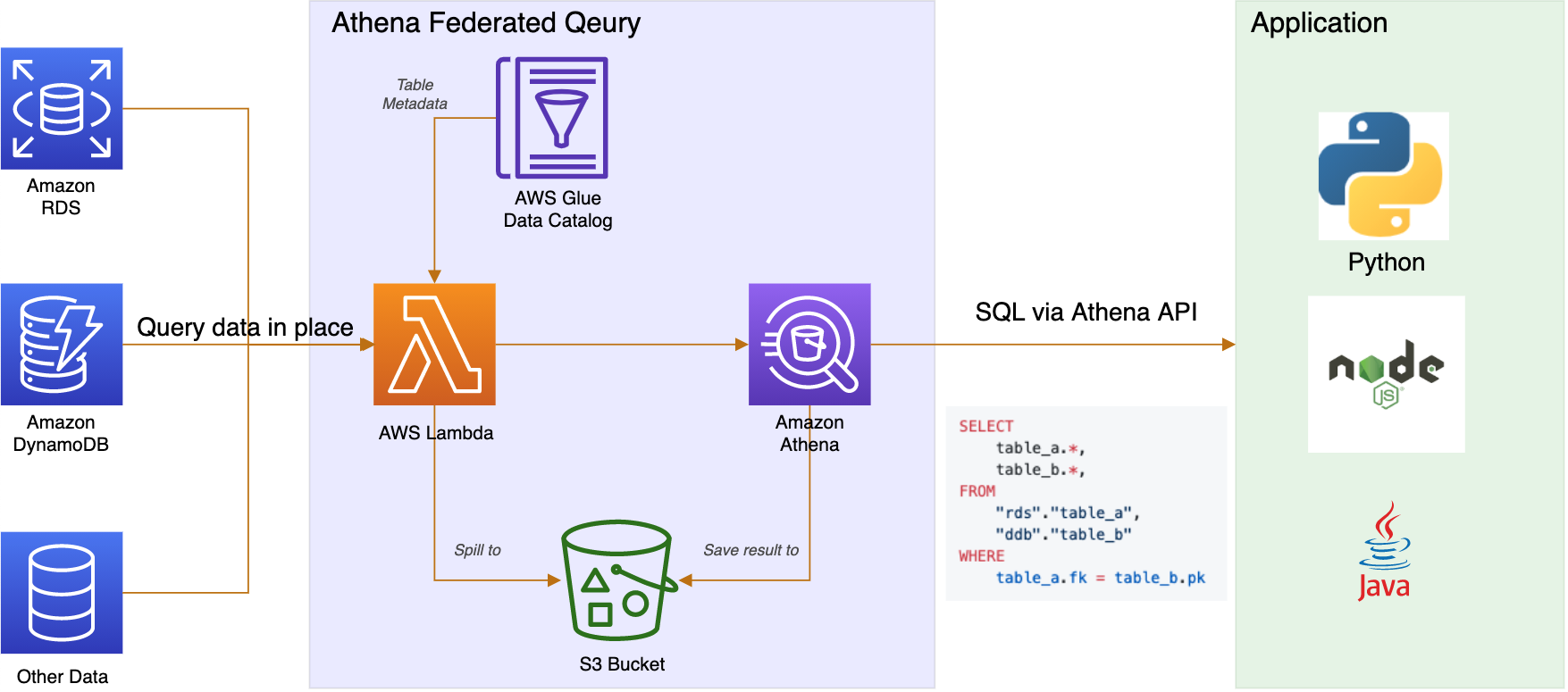
At the heart of this solution is Amazon Athena Federated Query. With this service, you can
- run standard SQL queries across data stored in relational, non-relational, object, and custom data sources.
- query data in place instead of moving data around. This is important as we know moving data is never an easy task.
- Write query script in programming languages like Java, Python… to analyze data via Athena APIs with JDBC driver.
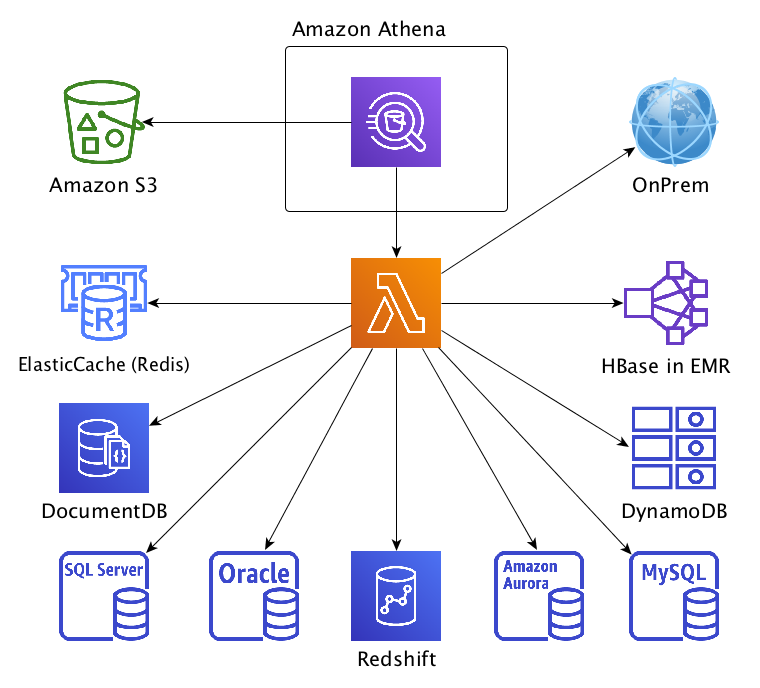
Athena uses data source connectors that run on AWS Lambda to run federated queries. A data source connector is a piece of code that can translate between your target data source and Athena. The connector automatically detects metadata about your data source before each query execution. Alternatively, you can use AWS Glue Data Catalog as the supplemental source of metadata for your connector. This can be handy when your data source doesn’t have it’s own source of metadata (e.g. DynamoDB).
Dashboard
To share analysis result across teams, a dashboard powered by Apache Echarts is generated daily and hosted on Github pages. At the back, a Jenkins job is running daily to execute query scripts written in Python and save query result to dashboard.
Conclusion
In this small experiment, we implemented a lightweight solution to analyze DynamoDB and RDS data in place using Amazon Athena Federated Query. The setup well fits our low-frequency, ad-hoc analysis use case and enables our engineers to query data in standard SQL or programming languages (e.g. Java, Python…) with JDBC driver.
Reference
AWS blog - DynamoDB Streams Use Cases and Design Patterns
Use case: How do you run analytical queries against data that is stored in DynamoDB?
Solution: For low frequency use cases, you can use Amazon Athena Federated Query or Amazon EMR with HiveQL to query directly against DynamoDB. DynamoDB is optimized for online, transactional use, where the majority of data operations are expected to be fully indexed (and materialized—to avoid variability in performance). For frequent analytical use, it’s generally better to export DynamoDB data (periodically or by ongoing stream-based propagation) into a data store such as Amazon Redshift, which is optimized by storage format to efficiently serve aggregations across large data sets.
